President Donald Trump recently proposed using Bitcoin to tackle the United States’ monumental $35 trillion national debt. While this suggestion has sparked excitement among cryptocurrency advocates, it has also raised serious questions about its feasibility and potential implications. Could Bitcoin be a viable solution, or is this merely an innovative but impractical idea?
The Case for Bitcoin in National Debt Management
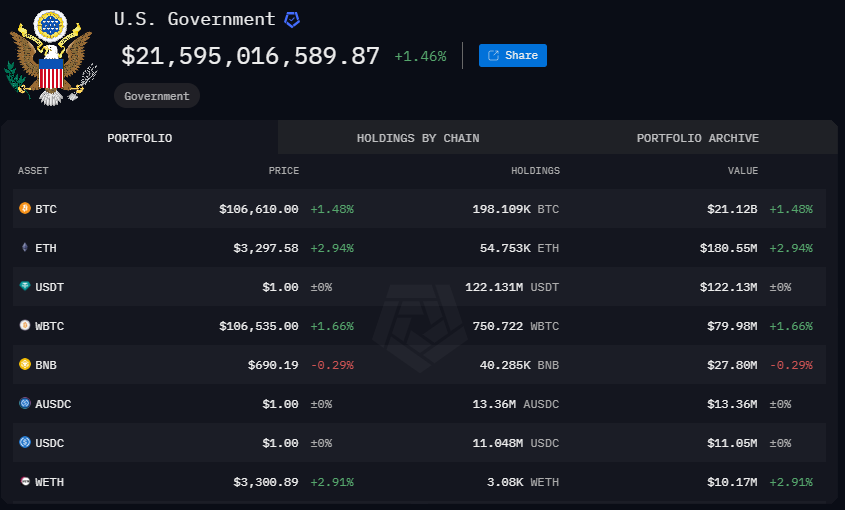
Bitcoin, the world’s first decentralized cryptocurrency, is often lauded for its potential to disrupt traditional financial systems. Advocates believe its inclusion in national reserves could bring several benefits:
1. Asset Diversification
Countries traditionally diversify their reserves with gold, foreign currencies, and government bonds. Adding Bitcoin could serve as a hedge against inflation in fiat currencies and protect reserves from geopolitical instability.
2. Modernization of Financial Systems
Adopting Bitcoin reflects a commitment to financial innovation, aligning the U.S. with the rapidly growing digital economy. This could bolster the nation’s position as a global leader in technology and innovation.
3. Growth Potential
As a relatively young asset class, cryptocurrencies like Bitcoin have shown exponential growth over the years. If Bitcoin continues to appreciate, it could provide significant returns, reducing the debt burden over time.
4. Enhanced Financial Sovereignty
Relying less on traditional banking systems and international debt markets could grant the U.S. greater financial independence. This could also minimize the influence of external factors on the economy.
Global Precedents for Cryptocurrency Adoption
Several nations have already begun exploring the integration of cryptocurrencies into their financial systems, albeit with mixed results:
- El Salvador: The first country to recognize Bitcoin as legal tender, integrating it into national reserves. The move attracted global attention, though it remains controversial.
- Ukraine: Cryptocurrencies are part of Ukraine’s modernization efforts, signaling a forward-thinking approach to financial management.
- China: While restricting cryptocurrency trading, China remains a major player in Bitcoin mining, influencing the global supply chain.
Challenges and Risks
Despite its potential, Bitcoin poses significant challenges as a tool for national debt management:
1. Volatility
Bitcoin’s price is notoriously unstable, making it a risky asset for managing something as critical as national debt. Sharp price fluctuations could exacerbate financial challenges rather than alleviate them.
2. Regulatory and Legal Hurdles
Bitcoin’s current status in the U.S. does not allow it to be used for settling national debts. Implementing such a strategy would require significant legislative reforms, introducing complex legal and tax considerations.
3. Public Trust and Perception
The general public may view Bitcoin investments as speculative rather than sound fiscal policy. Building trust would require robust education and transparent communication from policymakers.
4. Potential Systemic Risks
Over-reliance on cryptocurrencies could destabilize established financial systems, leading to unintended economic consequences.
Policy Considerations for Adoption
For Bitcoin to be included in national debt management, policymakers must address several key areas:
- Strategic Allocation: Limiting exposure by designating a small percentage of reserves to cryptocurrencies.
- Comprehensive Regulation: Establishing clear and enforceable frameworks to mitigate risks.
- International Collaboration: Working with global financial institutions to ensure stability and consistency.
- Public Education: Promoting understanding of the benefits and risks of cryptocurrencies.
Conclusion: A Revolutionary Idea with Realistic Limitations
President Trump’s proposal to use Bitcoin to manage the national debt is undoubtedly innovative and reflects growing interest in digital assets as a financial tool. However, its implementation faces numerous obstacles, from regulatory challenges to the volatility of Bitcoin itself. While the concept may appeal to cryptocurrency enthusiasts and forward-thinking economists, it requires careful consideration and detailed planning to avoid unintended consequences.
For now, Bitcoin’s role in addressing the national debt remains speculative, serving more as a conversation starter than a concrete policy solution. Nonetheless, it highlights the need for governments to explore modern financial strategies as they navigate the challenges of the 21st century.
