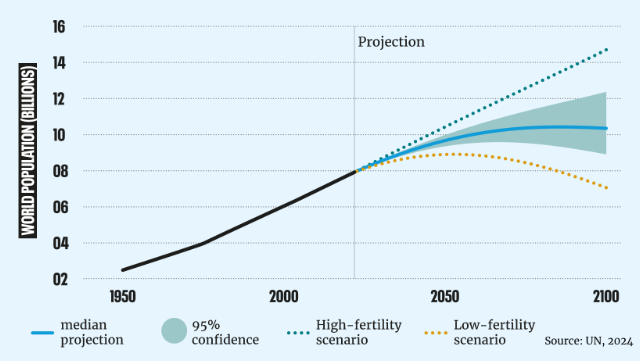
Declining birth rates are a pressing issue for many countries, particularly in developed regions. Below, we explore the causes, consequences, and policy measures aimed at mitigating this demographic trend.
Demographic Trends
Developed countries such as Japan, South Korea, Italy, and Germany are experiencing birth rates significantly below the replacement level of 2.1 children per woman. This shift results in aging populations, shrinking workforces, and economic challenges.
Key Factors Behind Declining Birth Rates
Economic Considerations
- Cost of Living: The rising expenses associated with childcare, education, and housing deter families from having more children.
- Work-Life Balance: Inadequate parental leave, expensive childcare, and rigid work conditions discourage parenthood.
Cultural Shifts
- Evolving Values: Modern societies prioritize personal freedom, career advancement, and lifestyle over traditional family roles.
- Urbanization: Urban living often leads to smaller families due to space and lifestyle constraints.
Social and Health Issues
- Changing Gender Roles: Societal expectations and the diminished role of extended families affect family planning.
- Reproductive Health: Delayed childbearing contributes to fertility challenges.
Consequences of Declining Birth Rates
Economic Impact
A shrinking workforce and increased demand for pensions and healthcare place immense pressure on social security systems and economic growth.
Social Changes
Labor shortages, rural depopulation, and an increased dependency ratio shift societal structures and strain public resources.
Policy Interventions
Many governments have implemented measures to combat declining birth rates:
- Financial Incentives: Childcare subsidies, tax breaks, and direct payments to families.
- Parental Leave Policies: Extending paid leave for both parents.
- Flexible Work Arrangements: Promoting work-life balance through telecommuting and part-time work.
Case Study: Japan
Japan exemplifies the challenges of an aging society and low birth rate. Its strategies include cautious immigration policies, automation in labor-intensive sectors, and encouraging workforce participation among women and the elderly. Family-supportive policies like childcare subsidies and family-friendly workplaces are also key elements of Japan’s approach.
In Summary
Addressing the issue of declining birth rates requires a multifaceted approach, blending economic, social, and cultural strategies. Collaboration between governments, businesses, and communities is essential to ensure sustainable population growth and economic stability.